What does Proton mean?
Definitions for Proton
ˈproʊ tɒnpro·ton
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word Proton.
Princeton's WordNet
protonnoun
a stable particle with positive charge equal to the negative charge of an electron
Wiktionary
protonnoun
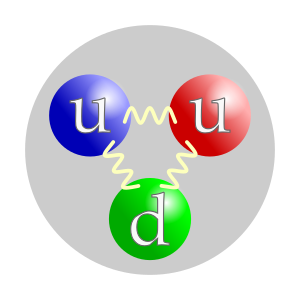
A positively charged subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom and determining the atomic number of an element; the nucleus of the most common isotope of hydrogen; composed of two up quarks and a down antiquark
Etymology: From πρῶτον, neuter of πρῶτος
Wikipedia
Proton
A proton is a subatomic particle, symbol p or p+, with a positive electric charge of +1e elementary charge and a mass slightly less than that of a neutron. Protons and neutrons, each with masses of approximately one atomic mass unit, are collectively referred to as "nucleons" (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the nucleus of every atom; they are a necessary part of the nucleus. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol Z). Since each element has a unique number of protons, each element has its own unique atomic number. The word proton is Greek for "first", and this name was given to the hydrogen nucleus by Ernest Rutherford in 1920. In previous years, Rutherford had discovered that the hydrogen nucleus (known to be the lightest nucleus) could be extracted from the nuclei of nitrogen by atomic collisions. Protons were therefore a candidate to be a fundamental particle, and hence a building block of nitrogen and all other heavier atomic nuclei. Although protons were originally considered fundamental or elementary particles, in the modern Standard Model of particle physics, protons are classified as hadrons, like neutrons, the other nucleon. Protons are composite particles composed of three valence quarks: two up quarks of charge +2/3e and one down quark of charge −1/3e. The rest masses of quarks contribute only about 1% of a proton's mass. The remainder of a proton's mass is due to quantum chromodynamics binding energy, which includes the kinetic energy of the quarks and the energy of the gluon fields that bind the quarks together. Because protons are not fundamental particles, they possess a measurable size; the root mean square charge radius of a proton is about 0.84–0.87 fm (or 0.84×10−15 to 0.87×10−15 m). In 2019, two different studies, using different techniques, have found the radius of the proton to be 0.833 fm, with an uncertainty of ±0.010 fm.At sufficiently low temperatures, free protons will bind to electrons. However, the character of such bound protons does not change, and they remain protons. A fast proton moving through matter will slow by interactions with electrons and nuclei, until it is captured by the electron cloud of an atom. The result is a protonated atom, which is a chemical compound of hydrogen. In vacuum, when free electrons are present, a sufficiently slow proton may pick up a single free electron, becoming a neutral hydrogen atom, which is chemically a free radical. Such "free hydrogen atoms" tend to react chemically with many other types of atoms at sufficiently low energies. When free hydrogen atoms react with each other, they form neutral hydrogen molecules (H2), which are the most common molecular component of molecular clouds in interstellar space.
ChatGPT
proton
A proton is a subatomic particle with a positive electric charge, found in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons in an atom's nucleus determines the atomic number, identifying the chemical element of the atom. It is one of the three main components of atoms, along with neutrons (no charge) and electrons (negative charge).
Wikidata
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol p or p+ and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number. The name proton was given to the hydrogen nucleus by Ernest Rutherford in 1920, because in previous years he had discovered that the hydrogen nucleus could be extracted from the nuclei of nitrogen by collision, and was thus a candidate to be a fundamental particle and building block of nitrogen, and all other heavier atomic nuclei. In the modern Standard Model of particle physics, the proton is a hadron, composed of quarks. Prior to that model becoming a consensus in the physics community, the proton was considered a fundamental particle. In the modern view, a proton is composed of three valence quarks: two up quarks and one down quark. The rest masses of the quarks are thought to contribute only about 1% of the proton's mass. The remainder of the proton mass is due to the kinetic energy of the quarks and to the energy of the gluon fields that bind the quarks together. Because the proton is not a fundamental particle, it possesses a physical size—although this is not perfectly well-defined since the surface of a proton is somewhat fuzzy, due to being defined by the influence of forces that do not come to an abrupt end. The proton is about 1.6–1.7 fm in diameter.
Matched Categories
Anagrams for Proton »
pronto
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of Proton in Chaldean Numerology is: 6
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of Proton in Pythagorean Numerology is: 8
Examples of Proton in a Sentence
I've been thinking about that old Zen conundrum what's the sound of one hand clapping My personal opinion--nothing. You don't have two hands, you don't have any clapping. It's as simple as that. Stars, galaxies, clapping hands, what's the point The point is that we all need somebody, whether you're a supercluster or a little proton, a yin or a yang. Everybody is hooked into everybody else.
We keep improving technology to do that better and better, so proton beam therapy is the next step.
Popularity rank by frequency of use
Translations for Proton
From our Multilingual Translation Dictionary
- بروتونArabic
- протонBulgarian
- প্রোটনBengali
- protóCatalan, Valencian
- protonCzech
- protonDanish
- ProtonGerman
- πρωτόνιοGreek
- protonoEsperanto
- protónSpanish
- protoiBasque
- پروتونPersian
- protoniFinnish
- protonFrench
- prótónIrish
- protónGalician
- પ્રાણુGujarati
- प्राणु, प्रोटॉनHindi
- protonHungarian
- պրոտոնArmenian
- protonIndonesian
- protonoIdo
- róteindIcelandic
- protoneItalian
- פרוטוןHebrew
- 陽子, プロトンJapanese
- ប្រូតុង, មូលាណូKhmer
- 陽性子, 양성자, 양자, 陽子Korean
- protonisLatin
- protonsLatvian
- iraohoMāori
- प्राणुMarathi
- protonMalay
- protonDutch
- protonNorwegian
- protonPolish
- prótonPortuguese
- protonRomanian
- протонRussian
- про̀то̄н, pròtōnSerbo-Croatian
- protonAlbanian
- protonSwedish
- mulasikTagalog
- protonTurkish
- protonVietnamese
- 质子Chinese
Get even more translations for Proton »
Translation
Find a translation for the Proton definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"Proton." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 26 Apr. 2024. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/Proton>.


Discuss these Proton definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In