What does mitochondrion mean?
Definitions for mitochondrion
ˌmaɪ təˈkɒn dri ən; -dri əmi·to·chon·dri·on
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word mitochondrion.
Princeton's WordNet
mitochondrion, chondriosomenoun
an organelle containing enzymes responsible for producing energy
Wiktionary
mitochondrionnoun
A spherical or ovoid organelle found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, contains genetic material separate from that of the host; it is responsible for the conversion of food to usable energy in the form of ATP.
Etymology: From +, diminutive of
Wikipedia
Mitochondrion
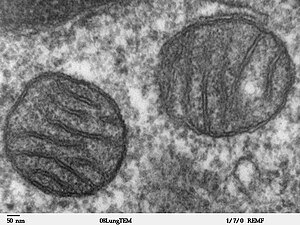
A mitochondrion (; pl. mitochondria) is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term mitochondrion was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name.Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia, parabasalids and diplomonads, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into other structures. One eukaryote, Monocercomonoides, is known to have completely lost its mitochondria, and one multicellular organism, Henneguya salminicola, is known to have retained mitochondrion-related organelles in association with a complete loss of their mitochondrial genome.Mitochondria are commonly between 0.75 and 3 μm2 in crossection, but vary considerably in size and structure. Unless specifically stained, they are not visible. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in other tasks, such as signaling, cellular differentiation, and cell death, as well as maintaining control of the cell cycle and cell growth. Mitochondrial biogenesis is in turn temporally coordinated with these cellular processes. Mitochondria have been implicated in several human disorders and conditions, such as mitochondrial diseases, cardiac dysfunction, heart failure and autism.The number of mitochondria in a cell can vary widely by organism, tissue, and cell type. A mature red blood cell has no mitochondria, whereas a liver cell can have more than 2000. The mitochondrion is composed of compartments that carry out specialized functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, cristae, and matrix. Although most of a eukaryotic cell's DNA is contained in the cell nucleus, the mitochondrion has its own genome ("mitogenome") that is substantially similar to bacterial genomes. This finding has led to general acceptance of the endosymbiotic hypothesis - that free-living prokaryotic ancestors of modern mitochondria permanently fused with eukaryotic cells in the distant past, evolving such that modern animals, plants, fungi, and other eukaryotes are able to respire to generate cellular energy.
ChatGPT
mitochondrion
Mitochondrion is a double-membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms. It is responsible for generating most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used as a source of chemical energy. Mitochondria are often called "powerhouses of the cell" due to their role in energy production. They also play a part in other processes such as signaling, cellular differentiation, cell death, as well as maintaining control of the cell cycle and cell growth.
Wikidata
Mitochondrion
Mitochondria are membrane-enclosed structures found in most eukaryotic cells. These organelles range from 0.5 to 1.0 micrometer in diameter. Mitochondria are sometimes described as "cellular power plants" because they generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate, used as a source of chemical energy. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in other tasks such as signaling, cellular differentiation, cell death, as well as the control of the cell cycle and cell growth. Mitochondria have been implicated in several human diseases, including mitochondrial disorders and cardiac dysfunction, and may play a role in the aging process. The word mitochondrion comes from the Greek μίτος, mitos, i.e. "thread", and χονδρίον, chondrion, i.e. "granule". Several characteristics make mitochondria unique. The number of mitochondria in a cell varies widely by organism and tissue type. Many cells have only a single mitochondrion, whereas others can contain several thousand mitochondria. The organelle is composed of compartments that carry out specialized functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, the intermembrane space, the inner membrane, and the cristae and matrix. Mitochondrial proteins vary depending on the tissue and the species. In humans, 615 distinct types of proteins have been identified from cardiac mitochondria, whereas in Murinae, 940 proteins encoded by distinct genes have been reported. The mitochondrial proteome is thought to be dynamically regulated. Although most of a cell's DNA is contained in the cell nucleus, the mitochondrion has its own independent genome. Further, its DNA shows substantial similarity to bacterial genomes.
Editors Contribution
mitochondrion
A structure with a specific function.
Mitochondrion has many purposes within the human body including signalling, regulation and synthesis.
Submitted by MaryC on December 26, 2020
Matched Categories
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of mitochondrion in Chaldean Numerology is: 1
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of mitochondrion in Pythagorean Numerology is: 4
Popularity rank by frequency of use
Translations for mitochondrion
From our Multilingual Translation Dictionary
- ميتوكوندريونArabic
- mitoxondriAzerbaijani
- митохондрияBulgarian
- মাইটোকন্ড্রিয়াBengali
- mitocondriCatalan, Valencian
- mitochondrieCzech
- Mitochondrion, MitochondriumGerman
- μιτοχόνδριοGreek
- mitocondriaSpanish
- mitokonderEstonian
- میتوکندریPersian
- mitokondrioFinnish
- mitochondrieFrench
- מיטוכונדריוןHebrew
- सूत्रकणिकाHindi
- mitokondriumHungarian
- միտոքոնդրիումArmenian
- hvatberiIcelandic
- mitocondrioItalian
- ミトコンドリア, 糸粒体Japanese
- 미토콘드리아Korean
- митохондријаMacedonian
- mitochondriumPolish
- mitocôndriaPortuguese
- митохондрияRussian
- митохондријеSerbo-Croatian
- mitokondrieSwedish
- ไมโทคอนเดรียThai
- sulidlawasTagalog
- mitokondriTurkish
- мітохондріяUkrainian
- ti thểVietnamese
Get even more translations for mitochondrion »
Translation
Find a translation for the mitochondrion definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"mitochondrion." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 12 May 2024. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/mitochondrion>.


Discuss these mitochondrion definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In