What does language family mean?
Definitions for language family
lan·guage fam·i·ly
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word language family.
Wiktionary
language familynoun
A set of languages which have evolved from a common ancestor.
Wikipedia
Language family
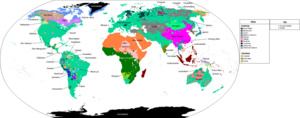
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestral language or parental language, called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in historical linguistics, which makes use of a metaphor comparing languages to people in a biological family tree, or in a subsequent modification, to species in a phylogenetic tree of evolutionary taxonomy. Linguists therefore describe the daughter languages within a language family as being genetically related.According to Ethnologue there are 7,151 living human languages distributed in 142 different language families. A living language is defined as one that is the first language of at least one person. The language families with the most speakers are: the Indo-European family, with many widely spoken languages native to Europe (such as English and Spanish) and South Asia (such as Hindi, Urdu and Bengali); and the Sino-Tibetan family, mainly due to the many speakers of Mandarin Chinese in China. Lyle Campbell (2019) identifies a total of 406 independent language families, including language isolates.There are also many dead languages which have no native speakers living, and extinct languages, which have no native speakers and no descendant languages. Finally, there are some languages that are insufficiently studied to be classified, and probably some which are not even known to exist outside their respective speech communities. Membership of languages in a language family is established by research in comparative linguistics. Sister languages are said to descend "genetically" from a common ancestor. Speakers of a language family belong to a common speech community. The divergence of a proto-language into daughter languages typically occurs through geographical separation, with the original speech community gradually evolving into distinct linguistic units. Individuals belonging to other speech communities may also adopt languages from a different language family through the language shift process.Genealogically related languages present shared retentions; that is, features of the proto-language (or reflexes of such features) that cannot be explained by chance or borrowing (convergence). Membership in a branch or group within a language family is established by shared innovations; that is, common features of those languages that are not found in the common ancestor of the entire family. For example, Germanic languages are "Germanic" in that they share vocabulary and grammatical features that are not believed to have been present in the Proto-Indo-European language. These features are believed to be innovations that took place in Proto-Germanic, a descendant of Proto-Indo-European that was the source of all Germanic languages.
Wikidata
Language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestor, called the proto-language of that family. The term 'family' comes from the tree model of language origination in historical linguistics, which makes use of a metaphor comparing languages to people in a biological family tree, or in a subsequent modification, to species in a phylogenetic tree of evolutionary taxonomy. No actual biological relationship between speakers is implied by the metaphor. As of early 2009, SIL Ethnologue catalogued 6,909 living human languages. A "living language" is simply one that is widely used as a primary form of communication by a specific group of living people. The exact number of known living languages varies from 5,000 to 10,000, depending generally on the precision of one's definition of "language", and in particular on how one classifies dialects. There are also many dead and extinct languages. Membership of languages in the same language family is established by comparative linguistics. Daughter languages are said to have a genetic or genealogical relationship; the former term is more modern, while the latter is more traditional. The evidence of linguistic relationship is found in observable shared characteristics that are not attributed to borrowing. Genealogically related languages present shared retentions, that is, features of the proto-language that cannot be explained by chance or borrowing. Membership in a branch or group within a language family is established by shared innovations, that is, common features of those languages that are not found in the common ancestor of the entire family. For example, Germanic languages are "Germanic" in that they share vocabulary and grammatical features that are not believed to have been present in the Proto-Indo-European language. These features are believed to be innovations that took place in Proto-Germanic, a descendant of Proto-Indo-European that was the source of all Germanic languages.
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of language family in Chaldean Numerology is: 9
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of language family in Pythagorean Numerology is: 8
Translations for language family
From our Multilingual Translation Dictionary
Get even more translations for language family »
Translation
Find a translation for the language family definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"language family." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 26 Apr. 2024. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/language+family>.


Discuss these language family definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In