What does diatom mean?
Definitions for diatom
ˈdaɪ ə təm, -ˌtɒmdi·atom
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word diatom.
Princeton's WordNet
diatomnoun
microscopic unicellular marine or freshwater colonial alga having cell walls impregnated with silica
Wiktionary
diatomnoun
One of the Diatomaceae, a family of minute unicellular algae having a siliceous covering of great delicacy.
Etymology: From διά + τέμνειν, i.e., "cut in half"
Wikipedia
Diatom
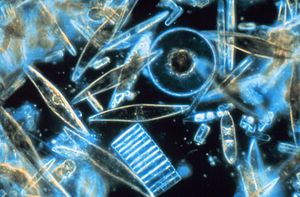
A diatom (Neo-Latin diatoma) is any member of a large group comprising several genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion metric tons of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile (800 m) deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of fresh-water lakes.Diatoms are unicellular organisms: they occur either as solitary cells or in colonies, which can take the shape of ribbons, fans, zigzags, or stars. Individual cells range in size from 2 to 200 micrometers. In the presence of adequate nutrients and sunlight, an assemblage of living diatoms doubles approximately every 24 hours by asexual multiple fission; the maximum life span of individual cells is about six days. Diatoms have two distinct shapes: a few (centric diatoms) are radially symmetric, while most (pennate diatoms) are broadly bilaterally symmetric. A unique feature of diatom anatomy is that they are surrounded by a cell wall made of silica (hydrated silicon dioxide), called a frustule. These frustules have structural coloration due to their photonic nanostructure, prompting them to be described as "jewels of the sea" and "living opals". Movement in diatoms primarily occurs passively as a result of both ocean currents and wind-induced water turbulence; however, male gametes of centric diatoms have flagella, permitting active movement to seek female gametes. Similar to plants, diatoms convert light energy to chemical energy by photosynthesis, but their chloroplasts were acquired in different ways.Unusually for autotrophic organisms, diatoms possess a urea cycle, a feature that they share with animals, although this cycle is used to different metabolic ends in diatoms. The family Rhopalodiaceae also possess a cyanobacterial endosymbiont called a spheroid body. This endosymbiont has lost its photosynthetic properties, but has kept its ability to perform nitrogen fixation, allowing the diatom to fix atmospheric nitrogen. Other diatoms in symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria are among the genera Hemiaulus, Rhizosolenia and Chaetoceros.Dinotoms are diatoms that have become endosymbionts inside dinoflagellates. Research on the dinoflagellates Durinskia baltica and Glenodinium foliaceum have shown that the endosymbiont event happened so recently, evolutionarily speaking, that their organelles and genome are still intact with minimum to no gene loss. The main difference between these and free living diatoms is that they have lost their cell wall of silica, making them the only known shell-less diatoms.The study of diatoms is a branch of phycology. Diatoms are classified as eukaryotes, organisms with a nuclear envelope-bound cell nucleus, that separates them from the prokaryotes archaea and bacteria. Diatoms are a type of plankton called phytoplankton, the most common of the plankton types. Diatoms also grow attached to benthic substrates, floating debris, and on macrophytes. They comprise an integral component of the periphyton community. Another classification divides plankton into eight types based on size: in this scheme, diatoms are classed as microalgae. Several systems for classifying the individual diatom species exist. Fossil evidence suggests that diatoms originated during or before the early Jurassic period, which was about 150 to 200 million years ago. The oldest fossil evidence for diatoms is a specimen of extant genus Hemiaulus in Late Jurassic aged amber from Thailand.Diatoms are used to monitor past and present environmental conditions, and are commonly used in studies of water quality. Diatomaceous earth (diatomite) is a collection of diatom shells found in the earth's crust. They are soft, silica-containing sedimentary rocks which are easily crumbled into a fine powder and typically have a particle size of 10 to 200 μm. Diatomaceous earth is used for a variety of purposes including for water filtration, as a mild abrasive, in cat litter, and as a dynamite stabilizer.
ChatGPT
diatom
A diatom is a type of single-celled algae that is characterized by a hard outer wall made of silica. They exist as either single cells or connected in a colony, are photosynthetic and often live in water environments, such as oceans, freshwater, and soil. They play a crucial role in the ecosystem by producing significant amounts of oxygen and serving as the primary food source for various marine and freshwater organisms. Diatoms are also used in scientific fields for environmental assessment due to their sensitivity to water conditions.
Webster Dictionary
Diatomnoun
one of the Diatomaceae, a family of minute unicellular Algae having a siliceous covering of great delicacy, each individual multiplying by spontaneous division. By some authors diatoms are called Bacillariae, but this word is not in general use
Diatomnoun
a particle or atom endowed with the vital principle
Etymology: [Gr. dia`tomos cut in two. See Diatomous.]
Wikidata
Diatom
Diatoms are a major group of algae, and are among the most common types of phytoplankton. Most diatoms are unicellular, although they can exist as colonies in the shape of filaments or ribbons, fans, zigzags, or stars. Diatoms are producers within the food chain. A unique feature of diatom cells is that they are encased within a cell wall made of silica called a frustule. These frustules show a wide diversity in form, but are usually almost bilaterally symmetrical, hence the group name. The symmetry is not perfect since one of the valves is slightly larger than the other allowing one valve to fit inside the edge of the other. Fossil evidence suggests that they originated during, or before, the early Jurassic Period. Only male gametes of centric diatoms are capable of movement by means of flagella. Diatom communities are a popular tool for monitoring environmental conditions, past and present, and are commonly used in studies of water quality.
Chambers 20th Century Dictionary
Diatom
dī′a-tom, n. one of an order of microscopic unicellular algæ, of the Diatomaceæ.—adj. Diatomā′ceous.—n. Diat′omite, diatomaceous earth. [Gr. diatomos—dia, through, temnein, to cut.]
Matched Categories
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of diatom in Chaldean Numerology is: 3
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of diatom in Pythagorean Numerology is: 8
Popularity rank by frequency of use
References
Translations for diatom
From our Multilingual Translation Dictionary
- diatomeaCatalan, Valencian
- KieselalgeGerman
- diatomeaSpanish
- piileväFinnish
- diatoméeFrench
- dà-dhadamScottish Gaelic
- 규조토Korean
- diatomee, kiezelwierDutch
- okrzemkaPolish
Get even more translations for diatom »
Translation
Find a translation for the diatom definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"diatom." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 26 Apr. 2024. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/diatom>.


Discuss these diatom definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In