What does neanderthal mean?
Definitions for neanderthal
niˈæn dərˌθɔl, neɪˈɑn dərˌtɑl; -ˌtɔl, -ˌtɑlne·an·derthal
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word neanderthal.
Princeton's WordNet
Neandertal man, Neanderthal man, Neandertal, Neanderthal, Homo sapiens neanderthalensisadjective
extinct robust human of Middle Paleolithic in Europe and western Asia
boorish, loutish, neanderthal, neandertal, oafish, swinishadjective
ill-mannered and coarse and contemptible in behavior or appearance
"was boorish and insensitive"; "the loutish manners of a bully"; "her stupid oafish husband"; "aristocratic contempt for the swinish multitude"
Neanderthal, Neanderthalian, Neandertaladjective
relating to or belonging to or resembling Neanderthal man
"Neanderthal skull"
GCIDE
Neanderthalnoun
(Anthropol.) A neanderthal human being; a member of the race Homo sapiens neanderthalensis; as, neanderthals were shorter than modern humans.
Neanderthalnoun
One resembling a neanderthal human; a troglodyte; a cave man.
Neanderthalnoun
Hence: (Fig.) A person of primitive, unenlightened or uneducated opinions or attitudes; one with a regressive social or political outlook; -- used disparagingly.
Wiktionary
neanderthalnoun
A primitive person or a person with old-fashioned ideas or who opposes change.
neanderthalnoun
(usually Neanderthal) A specimen of the now extinct species Homo neanderthalensis.
neanderthaladjective
Primitive, old-fashioned, opposed to change (in allusion to the now extinct species Homo neanderthalensis).
The capacity of the Neanderthal skull was 10% larger than that of modern humans.
Neanderthalnoun
A specimen of the now extinct species Homo neanderthalensis.
Neanderthalnoun
A primitive person.
Neanderthaladjective
Of or pertaining to Homines neanderthalenses.
The capacity of the Neanderthal skull was 10% larger than that of modern humans.
Neanderthaladjective
Old-fashioned, opposed to change (in allusion to Homo neanderthalensis).
Neanderthaladjective
Of or pertaining to the Neander Valley in Germany.
Etymology: From the name of the German valley where Neanderthal 1 was discovered in 1856. The (from w:Düssel, a small tributary of the River Rhine + tal) itself was renamed (from and/or) in the early 19 century to, and again in 1850 to w:Neanderthal, Germany; both names were in honour of the German Calvinist theologian and hymn writer Joachim Neander (1650–1680). The surname Neander is a Romanisation of the Greek translation of the original surname Neumann, for which reason Homo neanderthalensis is sometimes called New man in English.
Wikipedia
Neanderthal
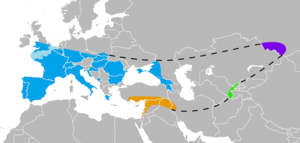
Neanderthals (; Homo neanderthalensis or H. sapiens neanderthalensis), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. The reasons for Neanderthal extinction remain a topic of discussion, the culprits include: demographic factors such as small population size and inbreeding; competitive replacement or assimilation into the modern human genome (i.e., Neanderthals were bred into extinction); great climatic change; disease; or a combination of these factors.It is unclear when the line of Neanderthals split from that of modern humans; studies have produced various intervals ranging from 315,000 to more than 800,000 years ago. The date of divergence of Neanderthals from their ancestor H. heidelbergensis is also unclear. The oldest potential Neanderthal bones date to 430,000 years ago, but the classification remains uncertain. Neanderthals are known from numerous fossils, especially from after 130,000 years ago. The type specimen, Neanderthal 1, was found in 1856 in the Neander Valley in present-day Germany. For much of the early 20th century, European researchers depicted Neanderthals as primitive, unintelligent, and brutish. Although knowledge and perception of them has markedly changed since then in the scientific community, the image of the unevolved caveman archetype remains prevalent in popular culture.Neanderthal technology was quite sophisticated. It includes the Mousterian stone-tool industry and ability to create fire and build cave hearths, make the adhesive birch bark tar, craft at least simple clothes similar to blankets and ponchos, weave, go seafaring through the Mediterranean, and make use of medicinal plants, as well as treat severe injuries, store food, and use various cooking techniques such as roasting, boiling, and smoking. Neanderthals made use of a wide array of food, mainly hoofed mammals, but also other megafauna, plants, small mammals, birds, and aquatic and marine resources. Although they were probably apex predators, they still competed with cave bears, cave lions, cave hyenas, and other large predators. A number of examples of symbolic thought and Palaeolithic art have been inconclusively attributed to Neanderthals, namely possible ornaments made from bird claws and feathers or shells, collections of unusual objects including crystals and fossils, engravings, music production (possibly indicated by the Divje Babe flute), and Spanish cave paintings contentiously dated to before 65,000 years ago. Some claims of religious beliefs have been made. Neanderthals were likely capable of speech, possibly articulate, although the complexity of their language is not known.Compared with modern humans, Neanderthals had a more robust build and proportionally shorter limbs. Researchers often explain these features as adaptations to conserve heat in a cold climate, but they may also have been adaptations for sprinting in the warmer, forested landscape that Neanderthals often inhabited. Nonetheless, they had cold-specific adaptations, such as specialised body-fat storage and an enlarged nose to warm air (although the nose could have been caused by genetic drift). Average Neanderthal men stood around 165 cm (5 ft 5 in) and women 153 cm (5 ft 0 in) tall, similar to pre-industrial modern humans. The braincases of Neanderthal men and women averaged about 1,600 cm3 (98 cu in) and 1,300 cm3 (79 cu in) respectively, which is within the range of the values for modern humans. The Neanderthal skull was more elongated and had smaller parietal lobes and cerebellum, morphological traits used to assign specimens to species. The total population of Neanderthals remained low, proliferating weakly harmful gene variants and precluding effective long-distance networks. Despite this, there is evidence of regional cultures and thus of regular communication between communities. They may have frequented caves and moved between them seasonally. Neanderthals lived in a high-stress environment with high trauma rates, and about 80% died before the age of 40. The 2010 Neanderthal genome project's draft report presented evidence for interbreeding between Neanderthals and modern humans. It possibly occurred 316,000 to 219,000 years ago, but more likely 100,000 years ago and again 65,000 years ago. Neanderthals also appear to have interbred with Denisovans, a different group of archaic humans, in Siberia. Around 1–4% of genomes of Eurasians, Indigenous Australians, Melanesians, Native Americans, and North Africans is of Neanderthal ancestry, while the inhabitants of sub-Saharan Africa have only 0.3% of Neanderthal genes, save possible traces from early sapiens-to-Neanderthal gene flow and/or more recent back-migration of Eurasians to Africa. In all, about 20% of distinctly Neanderthal gene variants survive today. Although many of the gene variants inherited from Neanderthals may have been detrimental and selected out, Neanderthal introgression ap
ChatGPT
neanderthal
Neanderthal refers to an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. They are closely related to modern humans, sharing 99.7% of DNA. Known for their distinctive physical characteristics, such as a robust build and low forehead, Neanderthals were proficient hunters and are also recognized for their cultural practices, including probable use of language and early art forms.
Wikidata
Neanderthal
The Neanderthals or Neandertals are an extinct species or subspecies of the genus Homo which is closely related to modern humans. They are known from fossils, dating from the Pleistocene period, which have been found in Europe and parts of western and central Asia. The species is named after Neandertal, the location in Germany where it was first discovered. Neanderthals are classified either as a subspecies of Homo sapiens or as a separate species of the same genus. The first humans with proto-Neanderthal traits are believed to have existed in Europe as early as 600,000–350,000 years ago. When the Neanderthals went extinct is disputed. Fossils found in the Vindija Cave in Croatia have been dated to between 33,000 and 32,000 years old, and Neanderthal artefacts from Gorham's Cave in Gibraltar are believed to be less than 30,000 years ago, but a recent study has re-dated fossils at two Spanish sites as 45,000 years old, 10,000 years older than previously thought, and may cast doubt on recent dates at other sites. Cro-Magnon skeletal remains showing certain "Neanderthal traits" have been found in Lagar Velho and dated to 24,500 years ago, suggesting that there may have been an extensive admixture of the Cro-Magnon and Neanderthal populations in that region.
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of neanderthal in Chaldean Numerology is: 4
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of neanderthal in Pythagorean Numerology is: 3
Examples of neanderthal in a Sentence
We’re not in the same Neanderthal-type environment.
We've found associations with sensitive neuropsychiatric diseases and addiction( and Neanderthal gene variants), which are primed for people to emotionally connect with when they're looking for an explanation for why they or their loved one is struggling.
We see a lot less compared to the rest of the genome, you’re going along the genome and there is the X chromosome or there are genes expressed in testes. Basically, these parts of the genome have less Neanderthal or Denisovan.
We can't blame Neanderthals for Covid. That's a damaging response, and that's why I want to emphasize so much the social and environmental factors are the real things that people should be worrying about, that said, as a geneticist, I think it is important to know the evolutionary history of the genetic variants we find that do have effects on traits. The effects of Neanderthal DNA traits are detectable, but they're modest.
I think the Science paper is a remarkable technical achievement and opens up many possibilities for future work in Eurasia on caves with no Neanderthal( or Denisovan) fossils.
Popularity rank by frequency of use
Translations for neanderthal
From our Multilingual Translation Dictionary
- الإنسان البدائيArabic
- neandertalCatalan, Valencian
- neandrtálecCzech
- NeandertalerGerman
- neandertalulo, neandertala homoEsperanto
- neandertalSpanish
- وابسته به انسان غارنشینPersian
- néandertalien, homme de NéandertalFrench
- неандерталецMacedonian
- неандерталец, неандертальскийRussian
- neandertalareSwedish
- ஆதிகால மனிதர்களின்Tamil
- มนุษย์ยุคกลางThai
- نیندرتھلUrdu
Get even more translations for neanderthal »
Translation
Find a translation for the neanderthal definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"neanderthal." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 26 Apr. 2024. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/neanderthal>.


Discuss these neanderthal definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In