What does economies of scale mean?
Definitions for economies of scale
economies of scale
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word economies of scale.
Wiktionary
economies of scalenoun
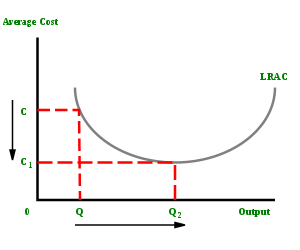
The characteristics of a production process in which an increase in the scale of the firm causes a decrease in the long run average cost of each unit.
Wikipedia
Economies of scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of output produced per unit of time. A decrease in cost per unit of output enables an increase in scale. At the basis of economies of scale, there may be technical, statistical, organizational or related factors to the degree of market control. This is just a partial description of the concept. Economies of scale apply to a variety of the organizational and business situations and at various levels, such as a production, plant or an entire enterprise. When average costs start falling as output increases, then economies of scale occur. Some economies of scale, such as capital cost of manufacturing facilities and friction loss of transportation and industrial equipment, have a physical or engineering basis. The economic concept dates back to Adam Smith and the idea of obtaining larger production returns through the use of division of labor. Diseconomies of scale are the opposite. Economies of scale often have limits, such as passing the optimum design point where costs per additional unit begin to increase. Common limits include exceeding the nearby raw material supply, such as wood in the lumber, pulp and paper industry. A common limit for a low cost per unit weight commodities is saturating the regional market, thus having to ship product uneconomic distances. Other limits include using energy less efficiently or having a higher defect rate. Large producers are usually efficient at long runs of a product grade (a commodity) and find it costly to switch grades frequently. They will, therefore, avoid specialty grades even though they have higher margins. Often smaller (usually older) manufacturing facilities remain viable by changing from commodity-grade production to specialty products.Economies of scale must be distinguished from economies stemming from an increase in the production of a given plant. When a plant is used below its optimal production capacity, increases in its degree of utilization bring about decreases in the total average cost of production. As noticed, among the others, by Nicholas Georgescu-Roegen (1966) and Nicholas Kaldor (1972) these economies are not economies of scale.
Wikidata
Economies of scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to size, with cost per unit of output generally decreasing with increasing scale as fixed costs are spread out over more units of output. Often operational efficiency is also greater with increasing scale, leading to lower variable cost as well. Economies of scale apply to a variety of organizational and business situations and at various levels, such as a business or manufacturing unit, plant or an entire enterprise. For example, a large manufacturing facility would be expected to have a lower cost per unit of output than a smaller facility, all other factors being equal, while a company with many facilities should have a cost advantage over a competitor with fewer. Some economies of scale, such as capital cost of manufacturing facilities and friction loss of transportation and industrial equipment, have a physical or engineering basis. The economic concept dates back to Adam Smith and the idea of obtaining larger production returns through the use of division of labor. Diseconomies of scale is the opposite. Economies of scale often have limits, such as passing the optimum design point where costs per additional unit begin to increase. Common limits include exceeding the nearby raw material supply, such as wood in the lumber, pulp and paper industry. A common limit for low cost per unit weight commodities is saturating the regional market, thus having to ship product uneconomical distances. Other limits include using energy less efficiently or having a higher defect rate.
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of economies of scale in Chaldean Numerology is: 7
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of economies of scale in Pythagorean Numerology is: 6
Examples of economies of scale in a Sentence
This has huge benefits in terms of economies of scale, innovation and sustainability. As a result, it is one of the most sophisticated and cleanest sites in the world.
As you get more economies of scale, you'll see more and more shifting over to natural gas, i think you are going to see larger and larger penetration of natural gas trucks in the marketplace. The economics are there.
There is a drive towards standardization but we believe that at this stage it isn't enough to generate big economies of scale.
SpiceJet has always been constrained by the lack of long-term orders. This will give us economies of scale and for our vendors and suppliers to see that we are growing.
Firms that are already in the indexing space want to have economies of scale so they can reduce their costs.
Translations for economies of scale
From our Multilingual Translation Dictionary
Get even more translations for economies of scale »
Translation
Find a translation for the economies of scale definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"economies of scale." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 29 Apr. 2024. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/economies+of+scale>.


Discuss these economies of scale definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In