What does sickle-cell anaemia mean?
Definitions for sickle-cell anaemia
sick·le-cel·l anaemi·a
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word sickle-cell anaemia.
Princeton's WordNet
sickle-cell anemia, sickle-cell anaemia, sickle-cell disease, crescent-cell anemia, crescent-cell anaemia, drepanocytic anemia, drepanocytic anaemianoun
a congenital form of anemia occurring mostly in blacks; characterized by abnormal blood cells having a crescent shape
Wiktionary
sickle-cell anaemianoun
A disease characterized by sickle-shaped red blood cells.
Wikipedia
sickle-cell anaemia
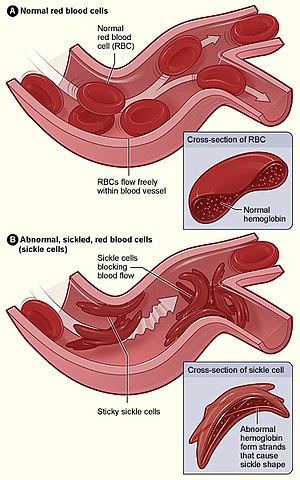
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red blood cells. This leads to a rigid, sickle-like shape under certain circumstances. Problems in sickle cell disease typically begin around 5 to 6 months of age. A number of health problems may develop, such as attacks of pain (known as a sickle cell crisis), anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections and stroke. Long-term pain may develop as people get older. The average life expectancy in the developed world is 40 to 60 years.Sickle cell disease occurs when a person inherits two abnormal copies of the β-globin gene (HBB) that makes haemoglobin, one from each parent. This gene occurs in chromosome 11. Several subtypes exist, depending on the exact mutation in each haemoglobin gene. An attack can be set off by temperature changes, stress, dehydration, and high altitude. A person with a single abnormal copy does not usually have symptoms and is said to have sickle cell trait. Such people are also referred to as carriers. Diagnosis is by a blood test, and some countries test all babies at birth for the disease. Diagnosis is also possible during pregnancy.The care of people with sickle cell disease may include infection prevention with vaccination and antibiotics, high fluid intake, folic acid supplementation, and pain medication. Other measures may include blood transfusion and the medication hydroxycarbamide (hydroxyurea). A small percentage of people can be cured by a transplant of bone marrow cells.As of 2015, about 4.4 million people have sickle cell disease, while an additional 43 million have sickle cell trait. About 80% of sickle cell disease cases are believed to occur in Sub-Saharan Africa. It also occurs to a lesser degree in parts of India, Southern Europe, West Asia, North Africa and among people of African origin (sub-Saharan) living in other parts of the world. In 2015, it resulted in about 114,800 deaths. The condition was first described in the medical literature by American physician James B. Herrick in 1910. In 1949, its genetic transmission was determined by E. A. Beet and J. V. Neel. In 1954, the protective effect against malaria of sickle cell trait was described.
ChatGPT
sickle-cell anaemia
Sickle-cell anaemia is a hereditary genetic blood disorder characterised by the presence of an abnormal form of haemoglobin, known as haemoglobin S, instead of haemoglobin A. The condition causes red blood cells to become misshapen and sickle-shaped instead of round. These sickle-shaped cells are less flexible and can block small blood vessels, leading to various health complications including infections, pain, anaemia, and organ damage. Sickle-cell anaemia is more common among people with Sub-Saharan African, South American, Caribbean, Central American, Saudi Arabian, Indian, or Mediterranean heritage.
Matched Categories
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of sickle-cell anaemia in Chaldean Numerology is: 4
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of sickle-cell anaemia in Pythagorean Numerology is: 9
Translation
Find a translation for the sickle-cell anaemia definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"sickle-cell anaemia." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 25 Apr. 2024. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/sickle-cell+anaemia>.


Discuss these sickle-cell anaemia definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In