What does receptors, antigen, b-cell mean?
Definitions for receptors, antigen, b-cell
re·cep·tors, anti·gen, b-cell
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word receptors, antigen, b-cell.
Wikipedia
receptors, antigen, b-cell
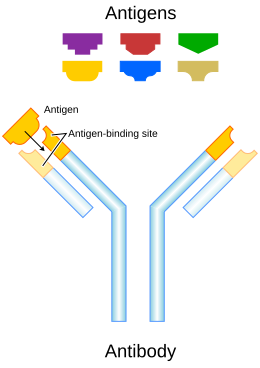
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can tag a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few variants, which define the antibody's class or isotype: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM. The constant region at the trunk of the antibody includes sites involved in interactions with other components of the immune system. The class hence determines the function triggered by an antibody after binding to an antigen, in addition to some structural features. Antibodies from different classes also differ in where they are released in the body and at what stage of an immune response. Together with B and T cells, antibodies comprise the most important part of the adaptive immune system. They occur in two forms: one that is attached to a B cell, and the other, a soluble form, that is unattached and found in extracellular fluids such as blood plasma. Initially, all antibodies are of the first form, attached to the surface of a B cell – these are then referred to as B-cell receptors (BCR). After an antigen binds to a BCR, the B cell activates to proliferate and differentiate into either plasma cells, which secrete soluble antibodies with the same paratope, or memory B cells, which survive in the body to enable long-lasting immunity to the antigen. Soluble antibodies are released into the blood and tissue fluids, as well as many secretions. Because these fluids were traditionally known as humors, antibody-mediated immunity is sometimes known as, or considered a part of, humoral immunity. The soluble Y-shaped units can occur individually as monomers, or in complexes of two to five units. Antibodies are glycoproteins belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. The terms antibody and immunoglobulin are often used interchangeably, though the term 'antibody' is sometimes reserved for the secreted, soluble form, i.e. excluding B-cell receptors.
U.S. National Library of Medicine
Receptors, Antigen, B-Cell
IMMUNOGLOBULINS on the surface of B-LYMPHOCYTES. Their MESSENGER RNA contains an EXON with a membrane spanning sequence, producing immunoglobulins in the form of type I transmembrane proteins as opposed to secreted immunoglobulins (ANTIBODIES) which do not contain the membrane spanning segment.
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of receptors, antigen, b-cell in Chaldean Numerology is: 7
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of receptors, antigen, b-cell in Pythagorean Numerology is: 7
Translation
Find a translation for the receptors, antigen, b-cell definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"receptors, antigen, b-cell." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 24 Apr. 2024. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/receptors%2C+antigen%2C+b-cell>.


Discuss these receptors, antigen, b-cell definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In