What does radioactive decay mean?
Definitions for radioactive decay
ra·dioac·tive de·cay
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word radioactive decay.
Princeton's WordNet
decay, radioactive decay, disintegrationnoun
the spontaneous disintegration of a radioactive substance along with the emission of ionizing radiation
Wiktionary
radioactive decaynoun
Any of several processes by which unstable nuclei emit subatomic particles and/or ionizing radiation and disintegrate into one or more smaller nuclei.
Wikipedia
Radioactive decay
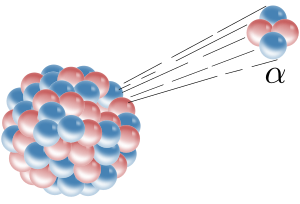
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha decay (α-decay), beta decay (β-decay), and gamma decay (γ-decay), all of which involve emitting one or more particles. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetism and nuclear force. A fourth type of common decay is electron capture, in which an unstable nucleus captures an inner electron from one of the electron shells. The loss of that electron from the shell results in a cascade of electrons dropping down to that lower shell resulting in emission of discrete X-rays from the transitions. A common example is iodine-125 commonly used in medical settings. Radioactive decay is a stochastic (i.e. random) process at the level of single atoms. According to quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay, regardless of how long the atom has existed. However, for a significant number of identical atoms, the overall decay rate can be expressed as a decay constant or as half-life. The half-lives of radioactive atoms have a huge range; from nearly instantaneous to far longer than the age of the universe. The decaying nucleus is called the parent radionuclide (or parent radioisotope), and the process produces at least one daughter nuclide. Except for gamma decay or internal conversion from a nuclear excited state, the decay is a nuclear transmutation resulting in a daughter containing a different number of protons or neutrons (or both). When the number of protons changes, an atom of a different chemical element is created. Alpha decay occurs when the nucleus ejects an alpha particle (helium nucleus). Beta decay occurs in two ways; In gamma decay a radioactive nucleus first decays by the emission of an alpha or beta particle. The daughter nucleus that results is usually left in an excited state and it can decay to a lower energy state by emitting a gamma ray photon. In neutron emission, extremely neutron-rich nuclei, formed due to other types of decay or after many successive neutron captures, occasionally lose energy by way of neutron emission, resulting in a change from one isotope to another of the same element. In electron capture, the nucleus may capture an orbiting electron, causing a proton to convert into a neutron. A neutrino and a gamma ray are subsequently emitted. In cluster decay and nuclear fission, a nucleus heavier than an alpha particle is emitted.By contrast there are radioactive decay processes that do not result in a nuclear transmutation. The energy of an excited nucleus may be emitted as a gamma ray in a process called gamma decay, or that energy may be lost when the nucleus interacts with an orbital electron causing its ejection from the atom, in a process called internal conversion. Another type of radioactive decay results in products that vary, appearing as two or more "fragments" of the original nucleus with a range of possible masses. This decay, called spontaneous fission, happens when a large unstable nucleus spontaneously splits into two (or occasionally three) smaller daughter nuclei, and generally leads to the emission of gamma rays, neutrons, or other particles from those products. In contrast, decay products from a nucleus with spin may be distributed non-isotropically with respect to that spin direction. Either because of an external influence such as an electromagnetic field, or because the nucleus was produced in a dynamic process that constrained the direction of its spin, the anisotropy may be detectable. Such a parent process could be a previous decay, or a nuclear reaction.For a summary table showing the number of stable and radioactive nuclides, see radionuclide. There are 28 naturally occurring chemical elements on Earth that are radioactive, consisting of 34 radionuclides (6 elements have 2 different radionuclides) that date before the time of formation of the Solar System. These 34 are known as primordial nuclides. Well-known examples are uranium and thorium, but also included are naturally occurring long-lived radioisotopes, such as potassium-40. Another 50 or so shorter-lived radionuclides found on Earth such as radium-226 and radon-222, are the products of decay chains that began with the primordial nuclides, or are the product of ongoing cosmogenic processes, such as the production of carbon-14 from nitrogen-14 in the atmosphere by cosmic rays. Radionuclides may also be produced artificially in particle accelerators or nuclear reactors, resulting in 650 of these with half-lives of over an hour, and several thousand more with even shorter half-lives. (See List of nuclides for a list of these sorted by half-life.)
ChatGPT
radioactive decay
Radioactive decay refers to a naturally occurring process in which unstable atomic nuclei lose energy, eventually achieving stability by emitting radiation or particles in the form of alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays. This transforms the radioactive material into a different substance, often a new element, over time. The rate of decay is measured in half-lives, the time it takes for half the unstable atoms in a sample to decay.
Wikidata
Radioactive decay
Radioactive decay, also known as nuclear decay or radioactivity, is the process by which a nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting particles of ionizing radiation. A material that spontaneously emits this kind of radiation — which includes the emission of energetic alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays — is considered radioactive. There are many different types of radioactive decay. A decay, or loss of energy, results when an atom with one type of nucleus, called the parent radionuclide, transforms to an atom with a nucleus in a different state, or to a different nucleus containing different numbers of protons and neutrons. Either of these products is named the daughter nuclide. In some decays the parent and daughter are different chemical elements, and thus the decay process results in nuclear transmutation. The first decay processes to be discovered were alpha decay, beta decay, and gamma decay. Alpha decay occurs when the nucleus ejects an alpha particle. This is the most common process of emitting nucleons, but in rarer types of decays, nuclei can eject protons, or specific nuclei of other elements. Beta decay occurs when the nucleus emits an electron or positron and a type of neutrino, in a process that changes a proton to a neutron or the other way around. The nucleus may capture an orbiting electron, converting a proton into a neutron. All of these processes result in nuclear transmutation.
Dictionary of Military and Associated Terms
radioactive decay
The decrease in the radiation intensity of any radioactive material with respect to time.
Matched Categories
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of radioactive decay in Chaldean Numerology is: 4
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of radioactive decay in Pythagorean Numerology is: 1
Examples of radioactive decay in a Sentence
Their radioactive decay dates when the rocks were buried in the cave when they fell in the entrance together with the fossils.
References
Translations for radioactive decay
From our Multilingual Translation Dictionary
Get even more translations for radioactive decay »
Translation
Find a translation for the radioactive decay definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"radioactive decay." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 23 Apr. 2024. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/radioactive+decay>.


Discuss these radioactive decay definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In