What does electric charge mean?
Definitions for electric charge
elec·tric charge
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word electric charge.
Princeton's WordNet
charge, electric chargenoun
the quantity of unbalanced electricity in a body (either positive or negative) and construed as an excess or deficiency of electrons
"the battery needed a fresh charge"
Wiktionary
electric chargenoun
the static electric energy of a charged body; the quantity of unbalanced positive or negative ions in or on an object; measured in coulombs
electric chargenoun
a quantum number of some subatomic particles which determines their electromagnetic interactions; by convention the electron has an electric charge of -1, the proton +1 and quarks have fractional charge
Wikipedia
Electric charge
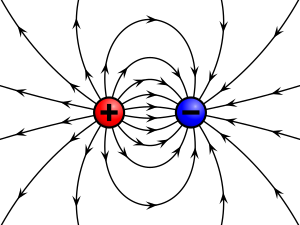
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be positive or negative (commonly carried by protons and electrons respectively). Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. An object with an absence of net charge is referred to as neutral. Early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still accurate for problems that do not require consideration of quantum effects. Electric charge is a conserved property; the net charge of an isolated system, the amount of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge, cannot change. Electric charge is carried by subatomic particles. In ordinary matter, negative charge is carried by electrons, and positive charge is carried by the protons in the nuclei of atoms. If there are more electrons than protons in a piece of matter, it will have a negative charge, if there are fewer it will have a positive charge, and if there are equal numbers it will be neutral. Charge is quantized; it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, about 1.602×10−19 coulombs, which is the smallest charge which can exist freely (particles called quarks have smaller charges, multiples of 1/3e, but they are only found in combination, and always combine to form particles with integer charge). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. Electric charges produce electric fields. A moving charge also produces a magnetic field. The interaction of electric charges with an electromagnetic field (combination of electric and magnetic fields) is the source of the electromagnetic (or Lorentz) force, which is one of the four fundamental forces in physics. The study of photon-mediated interactions among charged particles is called quantum electrodynamics.The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C) named after French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb. In electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah). In physics and chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. Chemistry also uses the Faraday constant as the charge on a mole of electrons. The lowercase symbol q often denotes charge.
ChatGPT
electric charge
Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. It can exist in one of two types, called positive and negative, and these charges generate and interact with electric fields. Electrical charges create electromagnetic forces, and the interaction between charges has been the foundation of electricity, magnetism and electromagnetism. An object with an absence of net charge is referred to as neutral. Early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate in practical situations.
Wikidata
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when close to other electrically charged matter. There are two types of electric charges, called positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object will be negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and will otherwise be positively charged or uncharged. The SI unit of electric charge is the coulomb, although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour, and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote a charge. The study of how charged substances interact is classical electrodynamics, which is accurate insofar as quantum effects can be ignored. The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces.−19
Matched Categories
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of electric charge in Chaldean Numerology is: 9
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of electric charge in Pythagorean Numerology is: 9
Examples of electric charge in a Sentence
That can cause what is known as self-initiated upward lightning, so the lightning occurs because you have charged at the tip of this wind turbine blade that is really close to the base of the cloud, and it’s really easy to get a connection of the electric charge.
Translations for electric charge
From our Multilingual Translation Dictionary
- càrregaCatalan, Valencian
- nábojCzech
- ladningDanish
- LadungGerman
- ηλεκτρικό φορτίοGreek
- elektra ŝargoEsperanto
- carga eléctricaSpanish
- شارژ الکتریکیPersian
- sähkövaraus, varausFinnish
- charge, charge électriqueFrench
- elektromos töltésHungarian
- caricaItalian
- 電荷Japanese
- បន្ទុកអគ្គីសនីKhmer
- ladingDutch
- încărcare, sarcină electricăRomanian
- зарядRussian
- električni nabojSlovene
Get even more translations for electric charge »
Translation
Find a translation for the electric charge definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"electric charge." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 23 Apr. 2024. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/electric+charge>.


Discuss these electric charge definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In