What does base pair mean?
Definitions for base pair
base pair
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word base pair.
Princeton's WordNet
base pairnoun
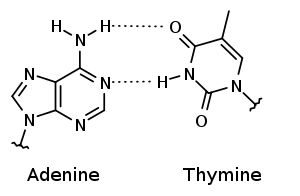
one of the pairs of chemical bases joined by hydrogen bonds that connect the complementary strands of a DNA molecule or of an RNA molecule that has two strands; the base pairs are adenine with thymine and guanine with cytosine in DNA and adenine with uracil and guanine with cytosine in RNA
Wiktionary
base pairnoun
In molecular biology, two nucleotides on opposite complementary DNA or RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds.
Wikipedia
Base pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA into RNA. Many DNA-binding proteins can recognize specific base-pairing patterns that identify particular regulatory regions of genes. Intramolecular base pairs can occur within single-stranded nucleic acids. This is particularly important in RNA molecules (e.g., transfer RNA), where Watson–Crick base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–uracil) permit the formation of short double-stranded helices, and a wide variety of non–Watson–Crick interactions (e.g., G–U or A–A) allow RNAs to fold into a vast range of specific three-dimensional structures. In addition, base-pairing between transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) forms the basis for the molecular recognition events that result in the nucleotide sequence of mRNA becoming translated into the amino acid sequence of proteins via the genetic code. The size of an individual gene or an organism's entire genome is often measured in base pairs because DNA is usually double-stranded. Hence, the number of total base pairs is equal to the number of nucleotides in one of the strands (with the exception of non-coding single-stranded regions of telomeres). The haploid human genome (23 chromosomes) is estimated to be about 3.2 billion bases long and to contain 20,000–25,000 distinct protein-coding genes. A kilobase (kb) is a unit of measurement in molecular biology equal to 1000 base pairs of DNA or RNA. The total number of DNA base pairs on Earth is estimated at 5.0×1037 with a weight of 50 billion tonnes. In comparison, the total mass of the biosphere has been estimated to be as much as 4 TtC (trillion tons of carbon).
ChatGPT
base pair
A base pair is a fundamental unit of the double helix structure of DNA, composed of two nucleic acids bound together by hydrogen bonds. The pairs are composed of either adenine with thymine or cytosine with guanine in DNA. In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil. The pairing of these bases enables the encoding and transfer of genetic information in organisms.
Wikidata
Base pair
Base pairs are the building blocks of the DNA double helix, and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, Watson-Crick base pairs allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is independent of its nucleotide sequence. The complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a backup copy of all genetic information encoded within double-stranded DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provide the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA, and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA into RNA. Many DNA-binding proteins can recognize specific base pairing patterns that identify particular regulatory regions of genes. Intramolecular base pairs can occur within single-stranded nucleic acids. This is particularly important in RNA molecules, where Watson-Crick base pairs permit the formation of short double-stranded helices, and a wide variety of non-Watson-Crick interactions allow RNAs to fold into a vast range of specific three-dimensional structures. In addition, base-paring between transfer RNA and messenger RNA forms the basis for the molecular recognition events that result in the nucleotide sequence of mRNA becoming translated into the amino acid sequence of proteins.
Matched Categories
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of base pair in Chaldean Numerology is: 5
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of base pair in Pythagorean Numerology is: 8
Translations for base pair
From our Multilingual Translation Dictionary
Get even more translations for base pair »
Translation
Find a translation for the base pair definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"base pair." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 25 Apr. 2024. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/base+pair>.


Discuss these base pair definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In