What does norepinephrine mean?
Definitions for norepinephrine
ˌnɔr ɛp əˈnɛf rɪn, -rinnor·ep·i·neph·rine
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word norepinephrine.
Princeton's WordNet
noradrenaline, norepinephrinenoun
a catecholamine precursor of epinephrine that is secreted by the adrenal medulla and also released at synapses
Wiktionary
norepinephrinenoun
A neurotransmitter found in the locus coeruleus which is synthesized from dopamine.
Wikipedia
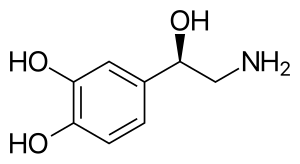
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin ad, "near", and ren, "kidney") is more commonly used in the United Kingdom, whereas "norepinephrine" (from Ancient Greek ἐπῐ́ (epí), "upon", and νεφρός (nephrós), "kidney") is usually preferred in the United States. "Norepinephrine" is also the international nonproprietary name given to the drug. Regardless of which name is used for the substance itself, parts of the body that produce or are affected by it are referred to as noradrenergic. The general function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in the so-called fight-or-flight response. In the brain, norepinephrine increases arousal and alertness, promotes vigilance, enhances formation and retrieval of memory, and focuses attention; it also increases restlessness and anxiety. In the rest of the body, norepinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal system, and inhibits voiding of the bladder and gastrointestinal motility. In the brain, noradrenaline is produced in nuclei that are small yet exert powerful effects on other brain areas. The most important of these nuclei is the locus coeruleus, located in the pons. Outside the brain, norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, as well as Merkel cells located in the skin. It is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands. Regardless of how and where it is released, norepinephrine acts on target cells by binding to and activating adrenergic receptors located on the cell surface. A variety of medically important drugs work by altering the actions of noradrenaline systems. Noradrenaline itself is widely used as an injectable drug for the treatment of critically low blood pressure. Stimulants often increase, enhance, or otherwise act as agonists of norepinephrine. Drugs such as cocaine and methylphenidate act as reuptake inhibitors of norepinephrine, as do some antidepressants, such as those in the SNRI class. One of the more notable drugs in the stimulant class is amphetamine, which acts as a dopamine and norepinephrine analog, reuptake inhibitor, as well as an agent that increases the amount of global catecholamine signaling throughout the nervous system by reversing transporters in the synapses. Beta blockers, which counter some of the effects of noradrenaline by blocking their receptors, are frequently used to treat glaucoma, migraine, and a range of cardiovascular problems. Alpha blockers, which counter a different set of noradrenaline effects, are used to treat several cardiovascular and psychiatric conditions. Alpha-2 agonists often have a sedating effect and are commonly used as anesthesia enhancers in surgery, as well as in treatment of drug or alcohol dependence. For reasons that are still unclear, some Alpha-2 drugs, such as guanfacine, have also been shown to be effective in the treatment of anxiety disorders and ADHD. Many important psychiatric drugs exert strong effects on noradrenaline systems in the brain, resulting in side-effects that may be helpful or harmful.
ChatGPT
norepinephrine
Norepinephrine is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter (chemical messenger in the brain) and hormone in the body that plays a key role in the "fight or flight" response to stress, as it increases heart rate, triggers the release of glucose from energy stores, and increases blood flow to skeletal muscle. In the brain, it is involved in arousal, attention, mood regulation and memory. Abnormal levels of norepinephrine have been implicated in a number of medical conditions, including mood disorders, hypertension, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Wikidata
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine, or noradrenaline, is a catecholamine with multiple roles including as a hormone and a neurotransmitter. Areas of the body that produce or are affected by norepinephrine are described as noradrenergic. The terms noradrenaline and norepinephrine are interchangeable, with noradrenaline being the common name in most parts of the world. However, to avoid confusion and achieve consistency, medical authorities have promoted norepinephrine as the favored nomenclature, and this is the term used throughout this article. One of the most important functions of norepinephrine is its role as the neurotransmitter released from the sympathetic neurons affecting the heart. An increase in norepinephrine from the sympathetic nervous system increases the rate of contractions. As a stress hormone, norepinephrine affects parts of the brain, such as the amygdala, where attention and responses are controlled. Along with epinephrine, norepinephrine also underlies the fight-or-flight response, directly increasing heart rate, triggering the release of glucose from energy stores, and increasing blood flow to skeletal muscle. It increases the brain's oxygen supply. Norepinephrine can also suppress neuroinflammation when released diffusely in the brain from the locus coeruleus.
U.S. National Library of Medicine
Norepinephrine
Precursor of epinephrine that is secreted by the adrenal medulla and is a widespread central and autonomic neurotransmitter. Norepinephrine is the principal transmitter of most postganglionic sympathetic fibers and of the diffuse projection system in the brain arising from the locus ceruleus. It is also found in plants and is used pharmacologically as a sympathomimetic.
Editors Contribution
norepinephrine
A type of hormone and neurotransmitter created within a living organism and the brain and body of an animal or human being.
Outside the brain, norepinephrine is used as a neurotransmitter by sympathetic ganglia located near the spinal cord or in the abdomen, and it is also released directly into the bloodstream by the adrenal glands.
Submitted by MaryC on January 30, 2020
Matched Categories
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of norepinephrine in Chaldean Numerology is: 1
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of norepinephrine in Pythagorean Numerology is: 4
Examples of norepinephrine in a Sentence
Toxic stress is prolonged exposure to hormones such as cortisol, epinephrine, norepinephrine -- fight or flight hormones -- and then inflammatory hormones, in a very young child, that disrupts brain development.
Norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine and cortisol can increase with stress from life events, work, relationships, finances and more.
Neurotransmitter chemicals like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine are involved in sexual response and orgasm, but they’re also influenced by medications that treat anxiety and depression.
Popularity rank by frequency of use
Translations for norepinephrine
From our Multilingual Translation Dictionary
Get even more translations for norepinephrine »
Translation
Find a translation for the norepinephrine definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"norepinephrine." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 25 Apr. 2024. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/norepinephrine>.


Discuss these norepinephrine definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In